What Is Gingivitis and How to Know if I Have It
Gingivitis is a very common gum condition that often goes unnoticed until it begins to cause discomfort or more visible symptoms. Understanding exactly what gingivitis is, how to identify its early signs, and knowing the best ways to manage and prevent it can make a big difference in maintaining your oral health.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about gingivitis—from causes and symptoms to diagnosis and treatment options.
What Is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, medically known as periodontal disease. It happens when plaque — that sticky film of bacteria that naturally forms on your teeth — isn’t cleaned away properly. If plaque builds up along your gumline, it irritates and inflames your gums.
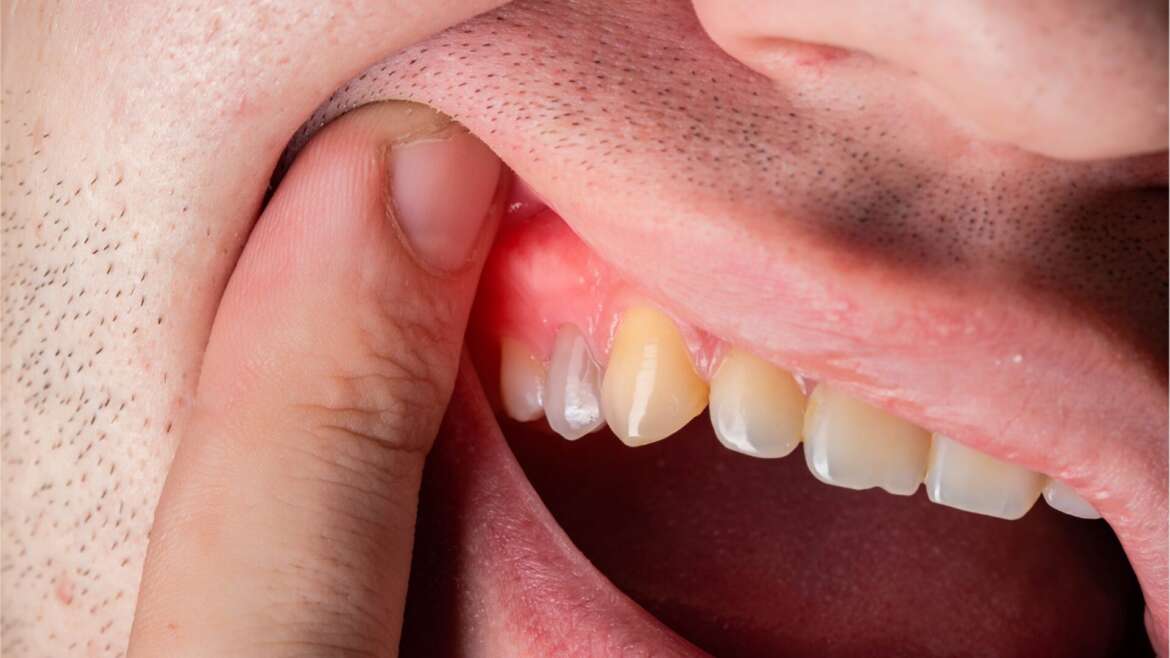
Healthy gums are usually firm, pale pink, and tightly hug your teeth. However, with gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen, tender, and prone to bleeding, especially when brushing or flossing.
This inflammation can be painless at first, which is why many people don’t realize they have gingivitis. However, if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis — a more severe gum disease that can cause lasting damage, including tooth loss.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
Knowing how to spot gingivitis early helps you take action before it worsens. Here are the key signs to watch for:
- Red or swollen gums: Your gums might look brighter or puffier than usual.
- Bleeding gums: Notice blood when you brush or floss? That’s a classic gingivitis warning.
- Tender or painful gums: Your gums may feel sore or sensitive to touch.
- Bad breath or unpleasant taste: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) or a bad taste in your mouth can be a sign.
- Receding gums: Gums pulling away from teeth, making them appear longer.
- Soft, spongy gums: Instead of firm and tight, your gums might feel loose or puffy.
- If you’ve seen any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to book a dental checkup to confirm and start treatment.
What Causes Gingivitis?
The main culprit behind gingivitis is plaque — a sticky layer of bacteria, saliva, food particles, and dead cells that constantly forms on teeth. If you miss brushing or flossing regularly, plaque settles along your gumline and between teeth.
After about 72 hours, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which toothbrushes can’t remove. Tartar buildup fuels more bacteria, causing your gums to get inflamed and irritated.
Aside from poor oral hygiene, several other factors can contribute to gingivitis:
- Smoking and tobacco use: These habits harm gum tissues and weaken the immune system.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can make gums ore sensitive.
- Certain medications: Drugs like calcium channel blockers, phenytoin, and anticoagulants may cause gum inflammation.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes and immune disorders reduce your ability to fight off infections.
- Dental appliances and crowded teeth: Ill-fitting bridges, braces, or uneven teeth make plaque harder to remove.
All these factors create an environment where plaque and bacteria can thrive, increasing your risk.
Types of Gingivitis
Gingivitis isn’t one-size-fits-all.
Dentists recognize several types based on causes:
- Plaque-induced gingivitis: By far the most common, caused by plaque buildup from inadequate cleaning.
- Hormonal gingivitis: Triggered by hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or puberty.
- Drug-induced gingivitis: Certain medications can cause gum overgrowth and inflammation.
- Eruptive gingivitis: Often seen in children, linked to teeth erupting and difficult cleaning in those areas.
Understanding the type can help tailor treatment effectively.
Diagnosing Gingivitis
Your dentist will examine your gums for redness, swelling, and bleeding. Gentle probing around your teeth measures pocket depths — spaces between gums and teeth.
Healthy gums usually have pockets between 1-3 mm deep; deeper pockets may suggest progressing disease.Dental X-rays might be taken to rule out bone loss, helping differentiate gingivitis from periodontitis. Regular dental visits every 6 to 12 months are vital to diagnose gingivitis early and treat it promptly.
How to Treat Gingivitis
Treating gingivitis focuses on removing plaque and tartar, reducing bacteria, and healing gums. Your dentist or dental hygienist will perform a professional cleaning, known as scaling and root planing, to remove buildup above and below the gumline.
At home, you’ll need to:
-
-
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
-
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
-
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash if recommended.
-
- Maintain regular dental cleanings.
-
In cases caused by medications or systemic issues, your dentist might coordinate with your doctor to manage those factors.
Preventing Gingivitis
Preventing gingivitis is practical and effective with consistent care:
- Good oral hygiene is the frontline defense to keep plaque from accumulating and your gums healthy.
- Brush twice daily for two minutes each time.
- Floss once a day.
- Avoid tobacco products.
- Visit your dentist regularly.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D.
Use mouthwash as advised.
Good oral hygiene is the frontline defense to keep plaque from accumulating and your gums healthy.
What If Gingivitis Is Left Untreated?
Gingivitis, when ignored, can advance to a more serious condition called periodontitis. This occurs as gum inflammation deepens and pockets form between the gums and teeth, creating spaces where bacteria accumulate and cause further infection. If untreated, the infection can destroy the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth, leading to loose teeth and even tooth loss.
The Progression from Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Unchecked gingivitis allows plaque to harden into tartar below the gumline, which can’t be removed by brushing alone. This creates an environment for aggressive bacteria that trigger chronic inflammation, breaking down the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. As pockets deepen, the damage worsens, and gums may recede, exposing more of the tooth roots and contributing to tooth sensitivity and decay.
Health Risks Beyond the Mouth
The effects of untreated gum disease don’t stop at your teeth. Research shows a connection between severe gum infections and systemic health issues, such as:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory illnesses
- Complications during pregnancy.
Chronic inflammation from gum disease can strain your immune response, increasing risks for these serious conditions.
Why Early Treatment Is Crucial
Early intervention with proper dental care can reverse gingivitis and stop damaging inflammation before periodontitis develops. Regular professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar, while at-home oral hygiene minimizes bacterial buildup. Maintaining these habits minimizes gum disease progression and protects not only your oral health but also your overall well-being.
How Midtown Dental Can Help
Taking care of your gums is more than just protecting your smile — it’s about maintaining your overall health and confidence. At Midtown Dental, our team is dedicated to helping you treat, manage, and prevent periodontal disease with compassion, expertise, and advanced care tailored to your needs.
Comprehensive Diagnosis
Our team begins each patient’s journey with a complete evaluation of gum and bone health. We use modern diagnostic tools — including periodontal probing and digital X-rays — to detect early signs of gum disease and design a treatment plan that’s unique to you.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For early to moderate stages of gum disease, our team provides gentle yet effective deep cleanings (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar buildup under the gums. We also offer targeted antibiotic therapies and personalized home-care guidance to keep your gums healthy between appointments.
Advanced and Minimally Invasive Procedures
When gum disease requires a deeper level of care, our team performs advanced treatments like pocket reduction (flap surgery), soft tissue grafts, bone regeneration, and laser-assisted therapy. These modern options promote healing, save natural teeth, and reduce discomfort — protecting both your smile and your confidence.
Preventive Care and Maintenance
At Midtown Dental, prevention is key. Our team partners with you to create personalized maintenance plans that include routine cleanings, frequent gum checkups, and education on proper oral hygiene. We also emphasize preventive care for patients with additional health concerns such as diabetes, heart conditions, or pregnancy.
Convenience and Trusted Support
Our clinic, located conveniently at Bloor-Yonge hub in downtown Toronto, offers same-day appointments, flexible scheduling, and a warm, welcoming environment. Our team values long-term relationships with patients, ensuring every visit feels supportive, comfortable, and effective.
Expert Dentists
Each doctor at Midtown Dental brings a strong background of training and experience, allowing us to offer a full range of general, cosmetic, and specialty dental services with confidence and quality you can trust.
Caring Dental Hygienists and Assistants
From your first dental cleaning to your ongoing care, our hygienists and dental assistants support your oral health journey with gentle hands and an understanding approach. They are here to answer your questions and help you feel at home in our office.
Friendly Administrative Team
Our reception and billing staff keep your visits smooth and stress-free. Whether it’s welcoming you with a smile or guiding you through appointments and insurance claims, they make your Midtown Dental experience as easy as possible.
A Team Focused on Your Care
The Midtown Dental team continually trains in the latest dental advances and works side-by-side to ensure you receive the highest quality personalized care. Your comfort, safety, and results are always our top priorities.
At Midtown Dental Centre, our goal is to make exceptional care accessible while building trust and confidence with every patient we treat. We’re not just restoring smiles — we’re restoring health, comfort, and peace of mind.
View the procedures we offer for more details.
FAQs About Gangivitis
How do I get rid of gingivitis?
The most effective way to get rid of gingivitis is through a thorough professional dental cleaning that removes plaque and tartar buildup, combined with diligent at-home oral care. Brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash help control bacteria that cause gum inflammation. In some cases, deeper cleanings like scaling and root planing may be necessary. Early treatment can fully reverse gingivitis and restore healthy gums.
What is the main cause of gingivitis?
Gingivitis primarily results from plaque buildup along the gumline due to poor oral hygiene. This sticky bacterial film irritates and inflames the gums, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding. Other contributing factors include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and medical conditions like diabetes, which can increase susceptibility. Tackling plaque is key to preventing gingivitis.
Can mouthwash reverse gingivitis?
Antimicrobial mouthwashes can support gingivitis treatment by reducing bacterial buildup and preventing plaque formation. However, mouthwash alone cannot cure gingivitis—it must be used in combination with consistent brushing, flossing, and professional dental care. Prescription mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine are especially helpful after professional cleanings. For best results, follow your dentist’s recommendations on mouthwash use.
Should you brush gingivitis?
Yes, gentle but thorough brushing is crucial for treating and preventing gingivitis. Brushing twice a day helps remove the plaque that causes gum inflammation. It’s important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid aggressive scrubbing to protect sensitive gums. Brushing along the gumline ensures that bacteria are effectively disrupted and removed.
Can salt water cure gingivitis?
Saltwater rinses can soothe inflamed gums and reduce bacterial levels, aiding the healing process in mild gingivitis cases. While saltwater won’t cure gingivitis alone, it’s a helpful adjunct to regular brushing, flossing, and professional treatments. A simple rinse of warm water and salt swished for 30 seconds can reduce swelling and discomfort. Use saltwater rinses several times daily for best support.
What toothpaste is best for gingivitis?
Toothpastes that contain fluoride and antibacterial agents like stannous fluoride or triclosan are best for managing gingivitis. These ingredients help reduce plaque buildup and soothe gum inflammation. Using toothpaste formulated specifically for gum health can enhance your daily oral hygiene routine. Always check for the American Dental Association (ADA) seal to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How long will gingivitis go away?
With proper treatment and oral care, gingivitis symptoms can improve within days and often resolve completely within one to two weeks. Professional cleaning combined with diligent brushing, flossing, and mouthwash use accelerates healing. Consistency is critical because untreated gingivitis can persist and worsen. Follow-up dental visits ensure the gums return to a healthy state.
What does gingivitis smell like?
Gingivitis often causes bad breath, which can smell unpleasant, sour, or metallic due to bacterial buildup and gum infection. This odor arises from volatile sulfur compounds produced by harmful oral bacteria. Consistent oral hygiene and treatment reduce the bacterial load and help eliminate the foul smell. Persistent bad breath can be an early warning sign of gingivitis.
What happens if gingivitis goes untreated?
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more serious gum disease that damages bone and connective tissues supporting teeth. This can lead to gum recession, tooth mobility, and ultimately tooth loss. Additionally, chronic gum infections may impact overall health by increasing risks for heart disease and diabetes complications. Early treatment prevents these severe outcomes.
How to tell if gingivitis is healing?
Healing gingivitis is indicated by reduced gum redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing. Gums regain a firm texture and a natural pink color as inflammation subsides. Improvement in breath odor and a decrease in gum tenderness also signal recovery. Regular dental checkups can confirm healing progress and guide ongoing care.
What is the fastest way to get rid of a gum infection?
The fastest way to treat a gum infection is prompt professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar, combined with meticulous oral hygiene at home. Your dentist may prescribe antimicrobial mouth rinses or antibiotics if the infection is severe. Saltwater rinses can soothe discomfort while reducing bacteria. Timely treatment halts infection and promotes quick recovery.
Can stress cause gingivitis?
Stress weakens the immune system, reducing your body’s ability to fight off bacterial infections, including those that cause gingivitis. It can also lead to neglect of oral hygiene or increased inflammation. Research shows a correlation between stress and the severity of gum disease. Managing stress alongside good dental care helps protect your gums.
Can Sensodyne cure gingivitis?
Sensodyne toothpaste helps reduce tooth sensitivity but does not cure gingivitis. While Sensodyne may soothe discomfort associated with exposed roots or sensitive gums, treating gingivitis requires plaque and tartar removal by brushing, flossing, and professional dental care. For gum health, look for toothpaste specifically formulated to combat gingivitis. Always consult your dentist for the best product for your needs.
Should I rinse after brushing?
It’s better to avoid rinsing your mouth with water immediately after brushing to allow fluoride from toothpaste to stay longer on your teeth. Fluoride strengthens enamel and helps prevent gum disease. If you use mouthwash, wait at least 30 minutes after brushing to avoid diluting these benefits. Following good rinsing habits enhances oral health.
Does gingivitis cause a fishy smell?
Gingivitis can cause bad breath that some describe as a fishy or sour smell, due to the metabolic byproducts of bacteria in infected gums. These volatile sulfur compounds are responsible for unpleasant odors. Effective treatment and thorough oral hygiene reduce these bacteria, eliminating the fishy smell. Persistent halitosis warrants a dental checkup for gingivitis evaluation.
What foods should I avoid with gingivitis?
Avoid sugary and starchy foods that fuel harmful bacteria and plaque buildup when managing gingivitis. Acidic drinks like soda and citrus juices can further irritate inflamed gums. Sticky snacks are especially problematic as they cling to teeth and gums, prolonging bacterial activity. Opt instead for fresh fruits, vegetables, and water to support gum healing.
Can other people smell gingivitis?
Gingivitis-related bad breath can be noticeable to others, especially when bacterial growth and gum infection cause persistent foul odors. Mouth odor due to gingivitis is often sour, musty, or fishy, which can affect social interactions. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking treatment reduces these odors, helping you feel more confident when talking to others.
Final Thoughts
Gingivitis may seem minor at first, but it’s a warning sign that your gums need attention. Ignoring it can lead to more serious gum disease with lasting effects on your smile and health. At Midtown Dental, our team is ready to help you spot the signs early, provide thorough exams, and deliver personalized, effective treatments to restore your gum health and prevent future problems.
Located just steps from the Yonge and Bloor subway station in downtown Toronto, we offer convenient same-day appointments and compassionate care when you need it most. Don’t wait to protect your gums and overall health—contact us today to schedule an exam and start your journey to a healthier, happier smile.